
Consequences: decreased cardiac output from reduced diastolic filling time, myocardial ischemia from increased oxygen demand and reduced coronary perfusion.Inappropriate causes: impaired autonomic control, POTS.Should not be treated unless underlying triggers have been ruled out, and it is deemed to be inappropriate.Endocrine abnormalities: hyperthyroidism, pheochromocytoma.Systolic heart failure: to compensate for low stroke volume.Sepsis: to augment CO to compensate for low SVR.Catecholamine surge: pain, fear, anger, stress.Arises almost always as a physiologic response or compensation to an underlying trigger, and this must be identified.To get started with the Qaly app for free, grab the Qaly app from the App Store or Play Store today.Narrow complex tachycardias are Supraventricular tachycardias, meaning only that they originate above the ventricles. On the Qaly app, human experts will interpret your ECGs within minutes for clarity and peace of mind. That's why we created the Qaly app for you and for the hundreds of millions of people around the world who live with heart palpitations and abnormal heart rhythms. If you still need help interpreting your ECGs, don't worry, we understand how scary and confusing it can be to experience irregular heartbeats. We hope this could be of some help to you. Well, that just about wraps up our guide on what Atrial Flutter looks like on your watch ECG. It's usually an age-related arrhythmia because it rarely occurs before the age of 50.Īs always, if you show signs of a potential Atrial Flutter, contact your healthcare provider immediately to rule out the presence of harmful underlying conditions. Here's Atrial Flutter with a variable ratio of F waves to QRS complexes.Ītrial Flutter raises your chance of having a stroke. įor clarity, take a look at these visual examples of Atrial Flutter ECGs. A regular R-R interval, although the rhythm can also be irregular.
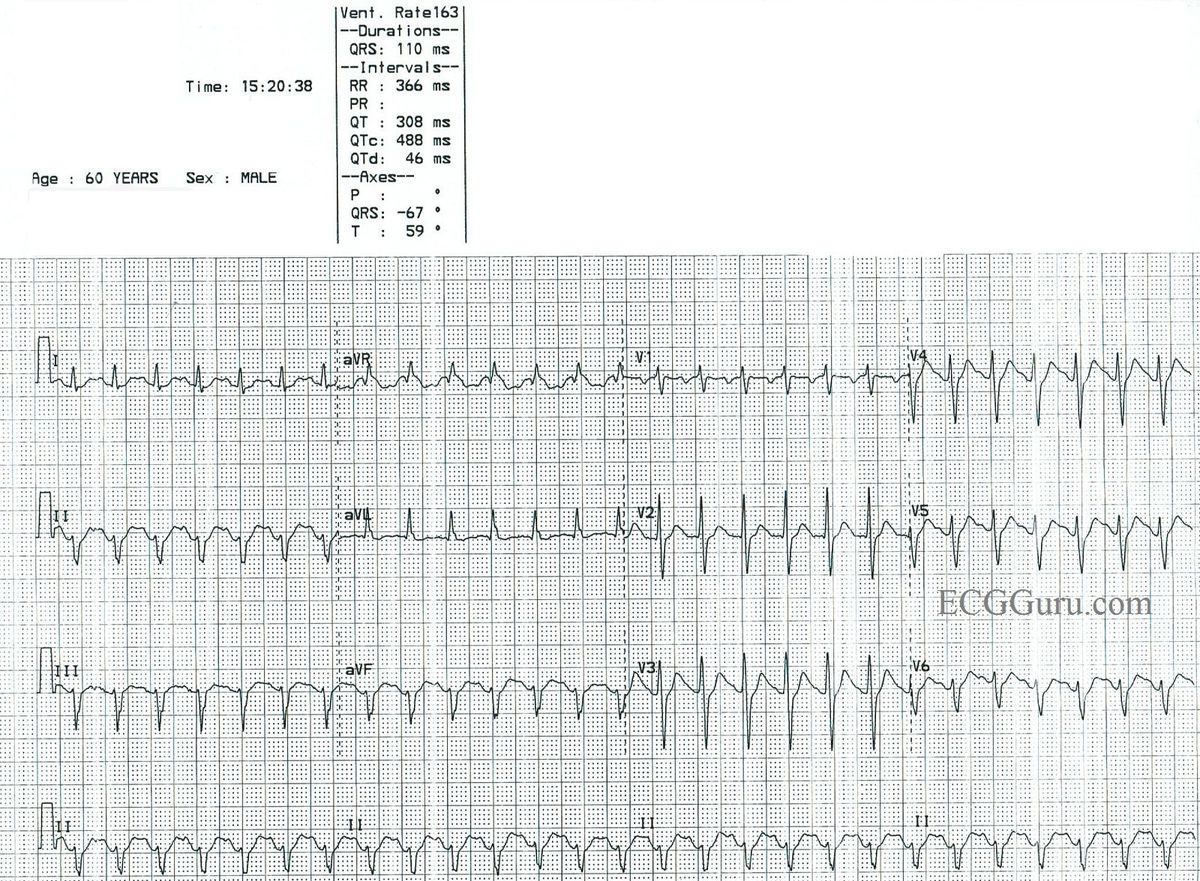
Flutter waves, also known as "F" waves, which appear in a “sawtooth” pattern.To identify Atrial Flutter on your ECG, look for these tell-tale signs:
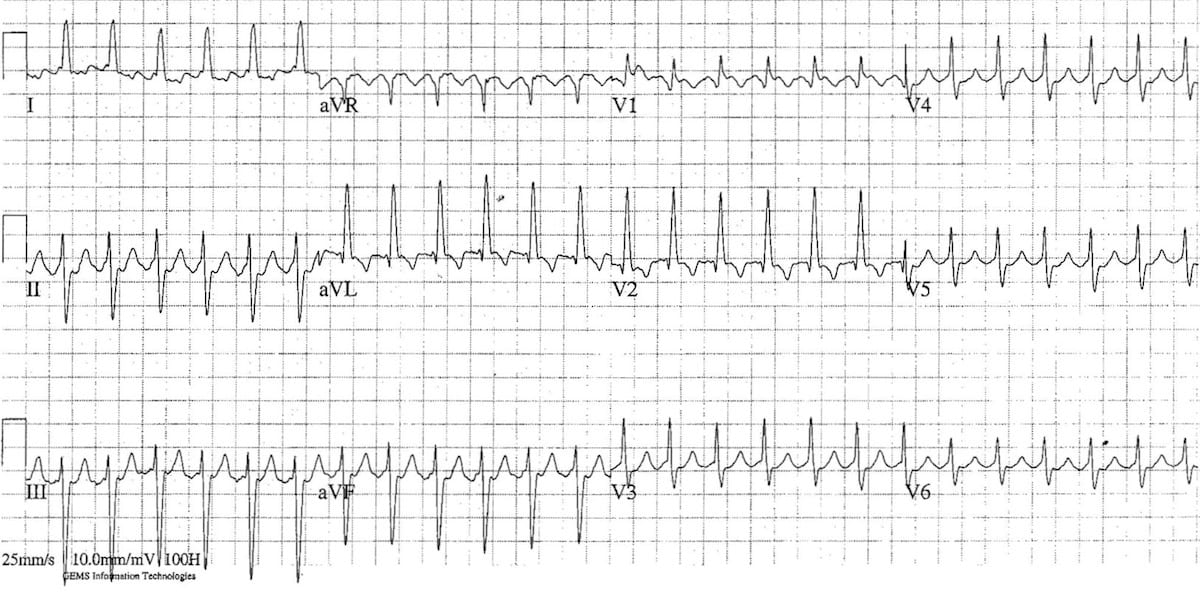
So What Does Atrial Flutter Look Like on My Watch ECG? On another note, Atrial Flutter is also more organized and less chaotic than Atrial Fibrillation. As a result, your heart beats too fast, but still in a steady rhythm. Instead, they move in a circle inside your atria. In Atrial Flutter, however, your heart's electrical impulses don't travel in a straight line from the top of your heart to the bottom of your heart. Then, that electrical signal travels from your heart's upper chambers, or atria, to your heart's lower chambers, or ventricles. Your heart typically produces that electrical signal from your "sinus node" to generate a normal heartbeat. To start, remember how your heart beats? It produces an electrical signal, which squeezes and unsqueezes your heart, which in turn pumps your blood to your lungs for oxygen and then out to the rest of your body. (If you're confident in your Atrial Flutter knowledge, though, skip on ahead to the next section for some visual examples of an Atrial Flutter ECG). Let's dive in.īefore trying to identify Atrial Flutter on your ECG, it's helpful to remind yourself what Atrial Flutter actually is. With your trusty watch ECG now in hand, you may be wondering, "What does Atrial Flutter look like on my watch ECG?" In this guide, we'll help you see Atrial Flutter on your watch ECG. In your quest to identify that irregular heart rhythm you just felt, you may have come across the term Atrial Flutter. The Ultimate Cardiologist's Guide to the Smartwatch ECG.How to Read an ECG: Stanford Cardiologist Explains.What PR, QRS, and QTc Intervals Mean on Your ECG.What Heart Palpitations and Irregular Heartbeats Look Like on Your ECG.What Unclassified EKG Means on Your KardiaMobile.What Inconclusive ECG Means on Your Samsung Watch.What Inconclusive ECG Means on Your Fitbit Watch.What Inconclusive ECG Means on Your Apple Watch.
Got other questions on your ECG? See the most popular Qaly guides on the ECG:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
